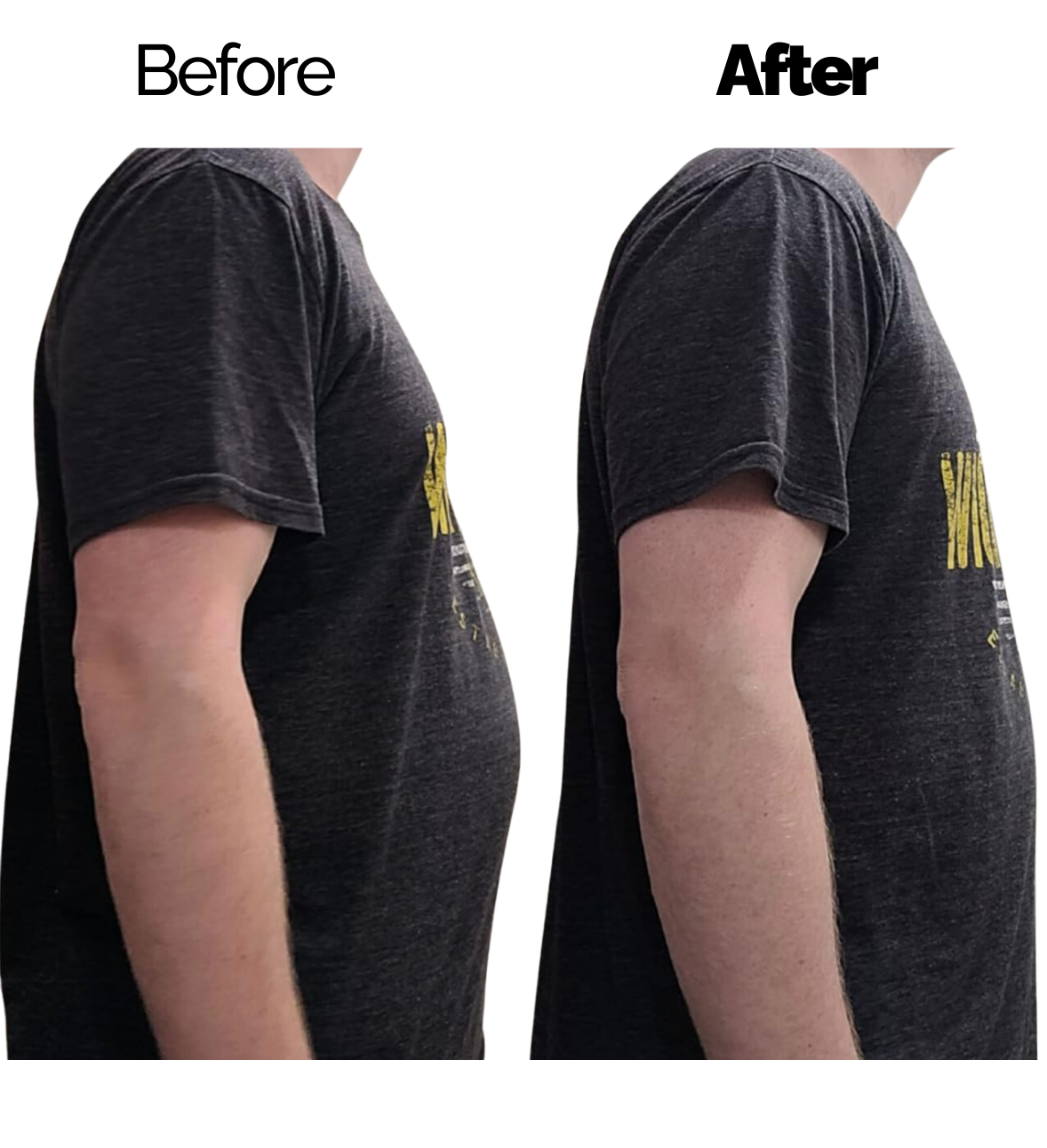
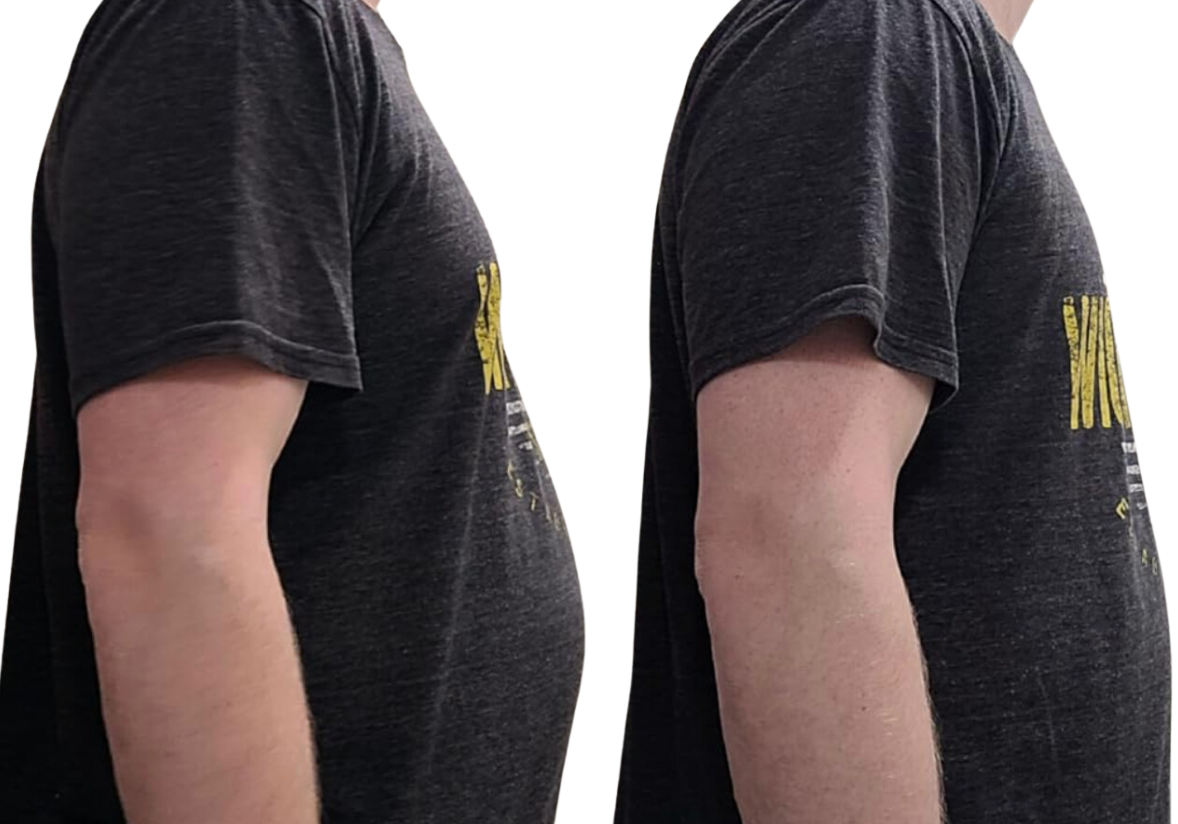
Everyone's body stores fat, with some spots being more prone to build-up. For guys, the chest can be one of these trouble areas. But it's crucial to tell the difference between regular chest fat and a condition called gynecomastia to get the right help. This article will dig into the reasons behind these issues, ways to treat them, and how to spot the difference between chest fat and gynecomastia.
What is chest fat?
Chest fat also called pseudogynecomastia, happens when too much fat builds up in the chest area. Several factors can cause this condition: not moving enough eating , hormone issues, or genes. Anyone can get chest fat, but people who weigh too much tend to have it more often.
When chest fat piles up, it makes the chest look bigger. But unlike gynecomastia, chest fat doesn't involve more breast gland tissue growing. It's made up of fat tissue. Keep in mind that you can get rid of chest fat by changing how you live, like eating better and working out more.
Causes of chest fat
Several things play a role in chest fat growth. A poor diet stands out as a key reason. Eating lots of processed foods sugary drinks, and foods high in saturated fat can make you gain weight. This extra weight often shows up as fat in different body parts, including the chest.
Not moving enough also has a big impact on chest fat. When you don't exercise much, you burn fewer calories. This can lead to weight gain and fat buildup in your chest area. Changes in hormones, like having low testosterone, can also cause chest fat to develop.
Also, genes have an impact on chest fat buildup. Some people might have a genetic tendency to store fat in their chest making it harder to lose through lifestyle changes by themselves.
How to lose chest fat through diet and exercise
If you want to lose chest fat, it's essential to add a healthy diet and workout plan. Begin by zeroing in on a well-rounded diet with lean proteins whole grains, fruits, and veggies. Try to stay away from processed foods sugary treats, and drinks as much as you can.
When it comes to working out, you need to mix cardio and strength training. Cardio exercises like running, swimming, or biking help you burn calories and cut down on body fat. Strength training moves such as push-ups, chest presses, and dumbbell flyes work on your chest muscles and help shape and define the area.
Keep in mind that you can't just target chest fat through exercise alone. This is known as spot reduction, and it doesn't work. To cut down on chest fat, you need to take a well-rounded approach. This means lowering your overall body fat through a mix of diet and exercise.
What is gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia refers to the growth of breast gland tissue in males. This condition can affect one or both breasts and often stems from a hormone imbalance an increase in estrogen compared to testosterone. Males of any age can develop gynecomastia, from babies to grown men, and it may last for a short time or stick around.
Unlike chest fat, gynecomastia doesn't mainly result from extra fat buildup. It involves the growth of glandular breast tissue, which can make the chest feel firm or rubbery. Gynecomastia can cause guys to feel upset and self-conscious lowering their quality of life.
Causes of gynecomastia
Many things can cause gynecomastia, like hormone problems, drugs, health issues, and how you live. When hormones get out of balance, like too much estrogen or not enough testosterone, it can lead to gynecomastia. This can happen during puberty, as you get older, or because of some health problems.
Some medicines can make gynecomastia happen too. These include steroids drugs that block male hormones, and some pills for depression. Health problems like liver or kidney disease, or tumors, can mess up your hormones and cause gynecomastia.
Sometimes, doctors can't pinpoint why gynecomastia happens. They call this idiopathic gynecomastia. No matter the reason, you should see a doctor if you have gynecomastia.
How to treat gynecomastia - surgical and non-surgical options
Doctors choose how to treat gynecomastia based on how bad it is and what's causing it. For mild cases where extra fat is the main problem, doctors might tell you to change your diet and exercise more. But if gynecomastia sticks around or happens because breast tissue is growing too much, you might need surgery or other treatments.
Doctors often use liposuction to remove extra fat in men with gynecomastia. This surgery involves small cuts in the chest and a suction tool to take out the fat. When glandular breast tissue causes the problem, surgeons may need to cut it out. They do this by making cuts around the nipple area.
Men with gynecomastia can also try treatments without surgery. These include medicine and hormone therapy. Doctors might prescribe drugs like tamoxifen or clomiphene to shrink the breast tissue. Hormone therapy can help too. This treatment gives testosterone or blocks estrogen, depending on what's causing the hormone imbalance.
Chest fat vs. gynecomastia - how to tell them apart
Telling chest fat and gynecomastia apart can be tough, since both make the chest look bigger. But a few key things can help you spot the difference.
How the chest feels is a big clue. Chest fat is soft and squishy when you touch it just like extra fat anywhere else on your body. But gynecomastia feels firm or rubbery because of the gland tissue in there.
Another key difference lies in how the extra tissue spreads out. Fat in the chest covers the whole area , including the top and bottom parts. Gynecomastia however often looks more focused and centered around the nipple.
If you notice your chest has gotten bigger and you're not sure if it's just fat or gynecomastia, it's a good idea to check with a doctor. A medical expert can figure out what's really going on and point you toward the right ways to deal with it.
Getting medical advice for a larger chest
If your chest looks different and you're worried, whether it's extra fat or a condition called gynecomastia, you should talk to a doctor. A regular doctor or a plastic surgeon can check you out and tell you what might help.
When you see the doctor, they'll ask about your health history, look at your chest, and maybe run some tests. They might do blood work or take pictures to figure out why your chest is larger.
Keep in mind seeing a doctor is key to get the right diagnosis and treatment plan. Don't wait to reach out if you're concerned about how your chest looks.
Conclusion: Getting a grip on your chest's look
Knowing the contrast between chest fat and gynecomastia plays a key role in getting a grip on your chest's look. These conditions can both lead to a bigger chest, but their root causes and ways to treat them are quite different.
If chest fat is your issue changing your lifestyle can help. This means eating better and working out to cut down on body fat, including in your chest. But if you have gynecomastia, you might need surgery or other treatments, based on how bad it is and what's causing it.
No matter what your situation is, getting medical help is key to get the right diagnosis and treatment plan. A doctor can point you toward the best options to tackle your issues and help you get the chest look you want.
So, make your move today and talk to a doctor to take charge of how your chest looks and boost your self-assurance.