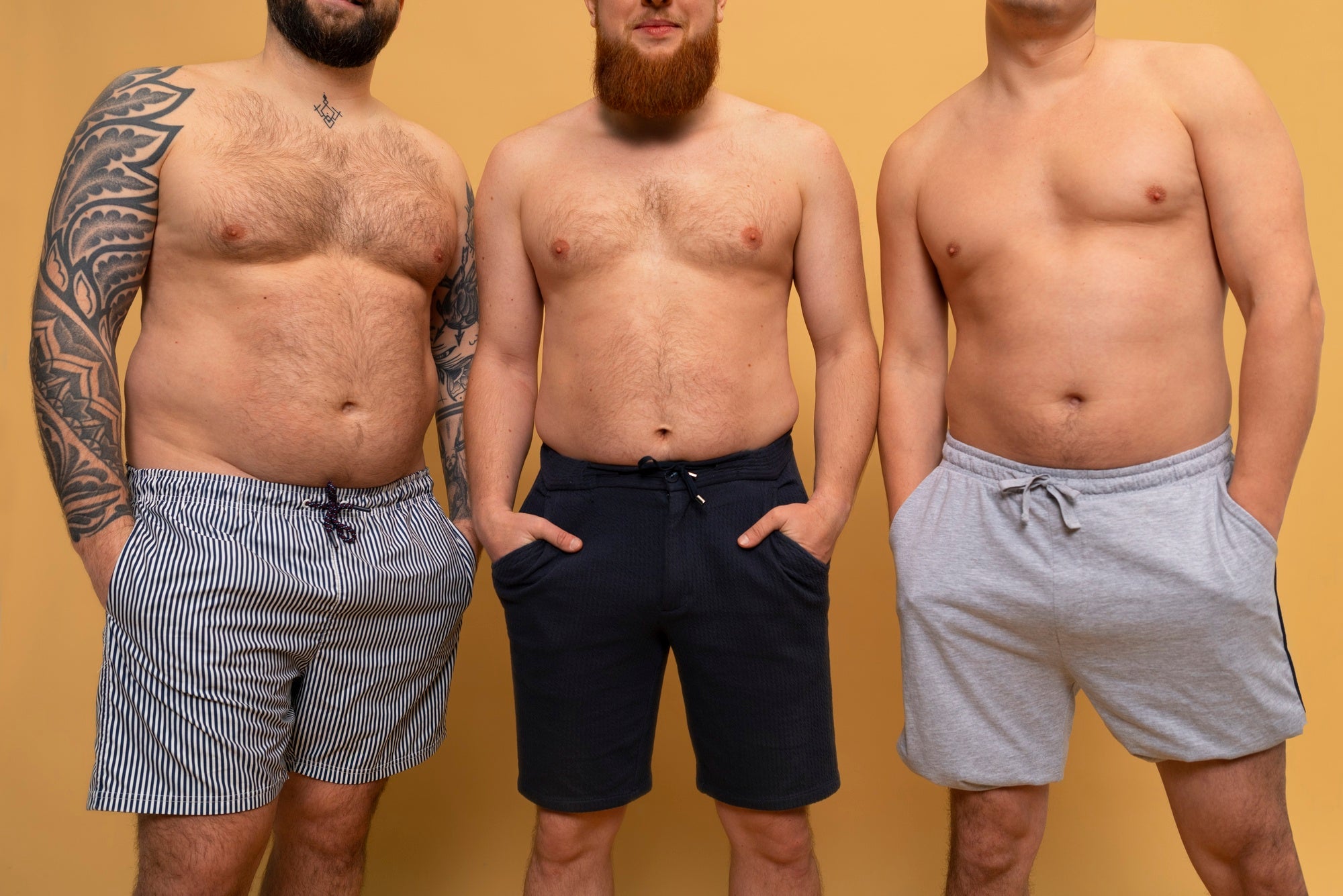
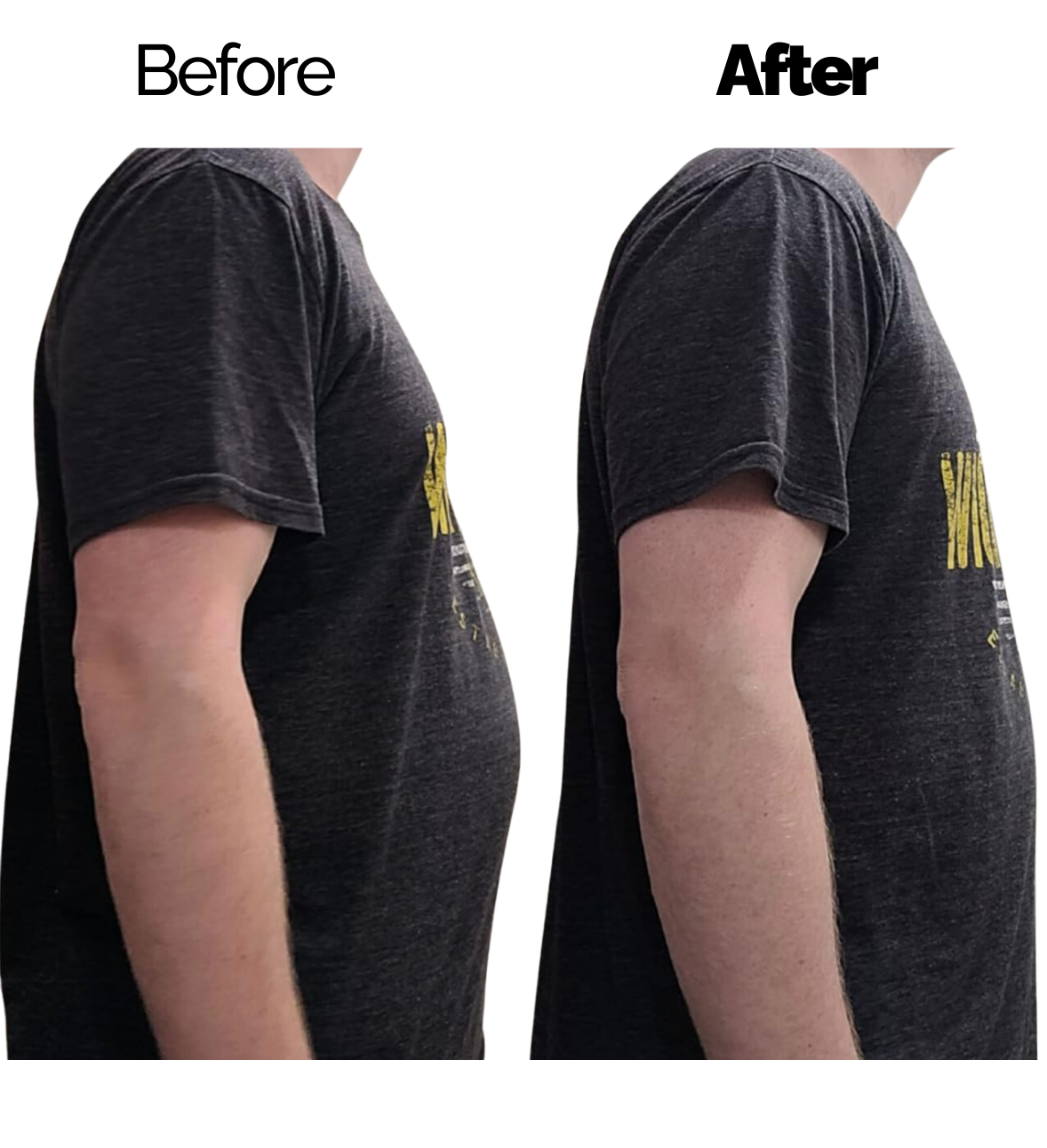
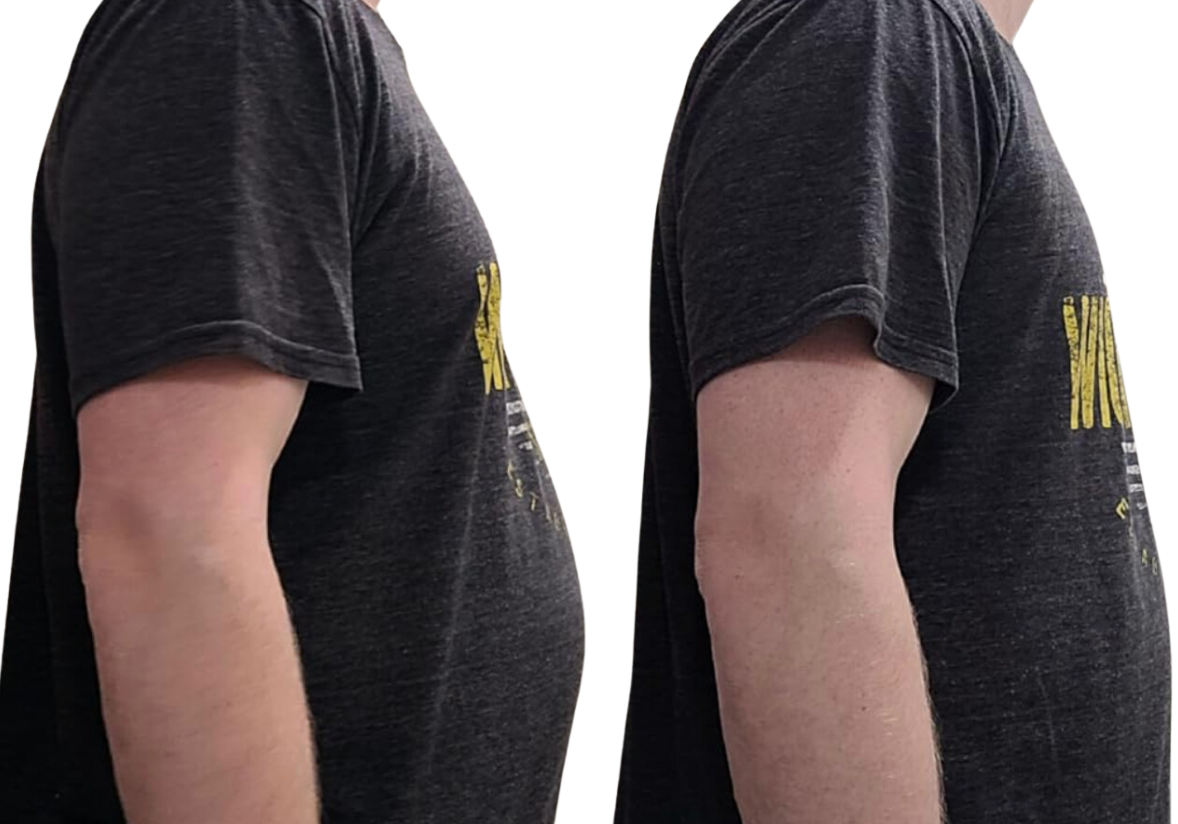
Gynecomastia refers to a health issue where male breast tissue grows larger. This happens when estrogen and testosterone levels become unbalanced leading to extra breast tissue growth. The condition can affect one or both breasts and is not dangerous. Even though it's harmless in most cases, it can make people feel upset and self-conscious.
What is pseudogynecomastia?
Pseudogynecomastia also called lipomastia or false gynecomastia, looks like gynecomastia but has a different root cause. Gynecomastia happens when breast tissue grows, but pseudogynecomastia occurs when fat builds up too much in the chest area. You'll see this condition more often in people who carry extra weight or deal with obesity, as the extra fat can make their chests look bigger.
Causes of gynecomastia
Many things can lead to gynecomastia. Hormone levels that are out of balance, like too much estrogen or not enough testosterone often play a big role. This can happen during the teen years when hormones are all over the place, or when you're older because of health issues or medications. Other things that might cause gynecomastia include problems with your liver or kidneys drinking too much alcohol, and using steroids to build muscle.
Causes of pseudogynecomastia
The main reason for pseudogynecomastia is too much body fat. When someone puts on weight, fat can build up in different parts of the body, including the chest. This extra fat can make it look like the breasts are bigger even though the breast tissue hasn't grown. Pseudogynecomastia happens more often in people who have a high body mass index (BMI) or who don't move around much. It also has a link to eating lots of processed foods and sugary drinks.
Symptoms of gynecomastia
The key sign of gynecomastia is breast tissue growth. The swollen area might hurt or feel tender when touched. Sometimes, fluid can leak from the nipple or the breast can ache. Gynecomastia can also mess with your head making you feel ashamed, self-aware, and unhappy with how you look. Keep in mind that gynecomastia isn't the same as breast cancer. Breast cancer shows up as a hard lump in the breast tissue.
Symptoms of pseudogynecomastia
The signs of pseudogynecomastia look like those of gynecomastia, but some key distinctions exist. Pseudogynecomastia causes chest enlargement because of extra fat buildup, not breast tissue growth. This results in a chest that feels soft and doughy instead of firm. People with pseudogynecomastia might also have symptoms linked to excess weight such as trouble breathing, tiredness, and achy joints.
Diagnosing gynecomastia
A doctor checks for gynecomastia by examining the patient and asking about their health background. They might also request extra tests, like blood work, to examine hormone levels and eliminate other possible reasons for breast growth. Sometimes, they may suggest imaging tests such as mammograms or ultrasounds, to take a closer look at the breast tissue.
Diagnosing pseudogynecomastia
Doctors diagnose pseudogynecomastia through a physical exam and by looking at the patient's medical history. Unlike gynecomastia, which involves breast tissue growth, pseudogynecomastia happens because of extra fat. So, the doctor might focus on checking how fat is spread in the chest area and other body parts. Sometimes, they might suggest more tests, like body composition analysis or imaging tests, to make sure of the diagnosis.
Treatment options for gynecomastia
Treatment choices for gynecomastia vary based on what's causing it and how bad it is. Sometimes enlarged breasts in men go away on their own without any help. But if the swelling sticks around or bothers someone, there are ways to treat it. These might include taking medicine balancing hormones, or having surgery. Doctors might give out drugs like tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors to slow down breast growth. For more serious cases, they might suggest surgery such as liposuction or removing breast tissue, to get rid of the extra bulk.
Treatment options for pseudogynecomastia
To treat pseudogynecomastia, doctors advise changing your lifestyle losing weight and cutting down body fat. You can do this by eating healthy and working out . Stick to a balanced diet with good nutrients to slim down and make your chest look smaller. Lifting weights can also build muscle and shape up your chest. Some people think about getting cosmetic surgery, like liposuction, to remove extra fat from their chest area.
Gynecomastia vs pseudogynecomastia: Key differences
Both gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia lead to bigger chests in men, but they're not the same thing. Gynecomastia happens when breast tissue grows often because hormones are out of whack. Pseudogynecomastia is different - it's when extra fat builds up in the chest area. You'll see gynecomastia more in teenage boys, while pseudogynecomastia shows up more in guys who are carrying extra weight. These conditions need different fixes too. Gynecomastia might need medicine or an operation, but pseudogynecomastia can often get better with changes to diet and exercise.
How to prevent gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia
To prevent gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia, you need to live a healthy life. This means working out often to keep your weight in check and cut down on body fat. It's also key to stay away from anabolic steroids or other drugs that can mess with your hormones. On top of that, you should watch your intake of alcohol and drugs, as these can lead to gynecomastia. By living a healthy balanced life, you can lower your chances of getting either gynecomastia or pseudogynecomastia.
Conclusion
To wrap up knowing the distinction between gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia has a significant impact on correct diagnosis and suitable treatment. Gynecomastia happens when breast tissue grows in males because of hormone imbalances, while pseudogynecomastia results from too much fat building up in the chest area. Each condition has different symptoms ways to diagnose, and options to treat, which shows how crucial it is to get medical advice for a proper check-up. People can lower their chances of developing both gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia by living a healthy life and taking a balanced approach to eating and working out.